What is Security Operation Center?

According to ibm.com security operations center is a team of information technology security professionals that monitors and organizations entire infrastructure 24/7 to detect cybersecurity events in real time and address them as quickly and as effectively as possible.
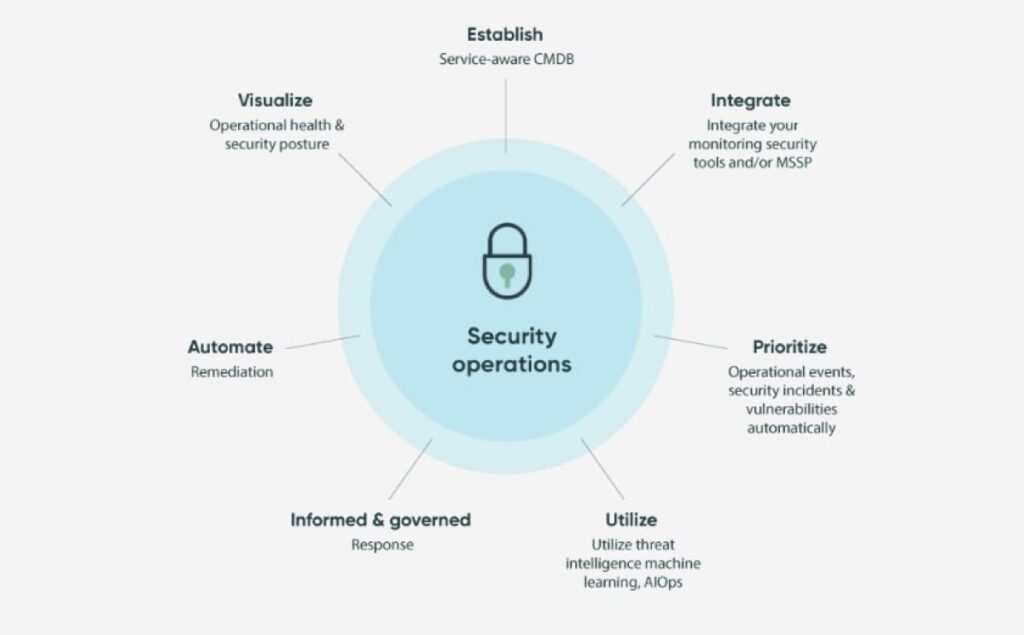
This branch in cybersecurity has to have preventative measures and security policies fast threat detection and faster more effective and cost-effective response to cyber security threats this can strengthen and organizations compliance with industry national and global privacy regulations.
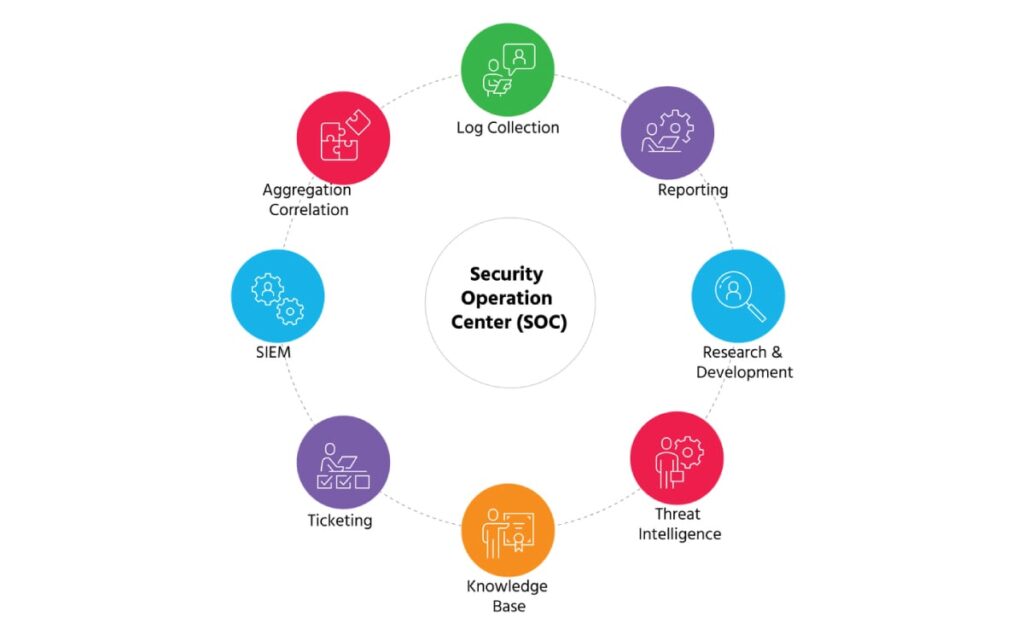
The activities and responsibilities of a SOC fall into three general categories:
1 preparation, planning and prevention – this can be achieved Through asset inventory, routine maintenance and preparation, incident response planning, regular testing, and staying current with the latest security solutions, technologies, and threat intelligence.
2 monitoring, detection, and response – Continuous around the clock monitoring through core monitoring detection and response technology such as security information and event management or SIEM, log management, threat detection, incident response.
3 recovery, refinement, and compliance – recovery and remediation, post mortem and refinement and compliance management
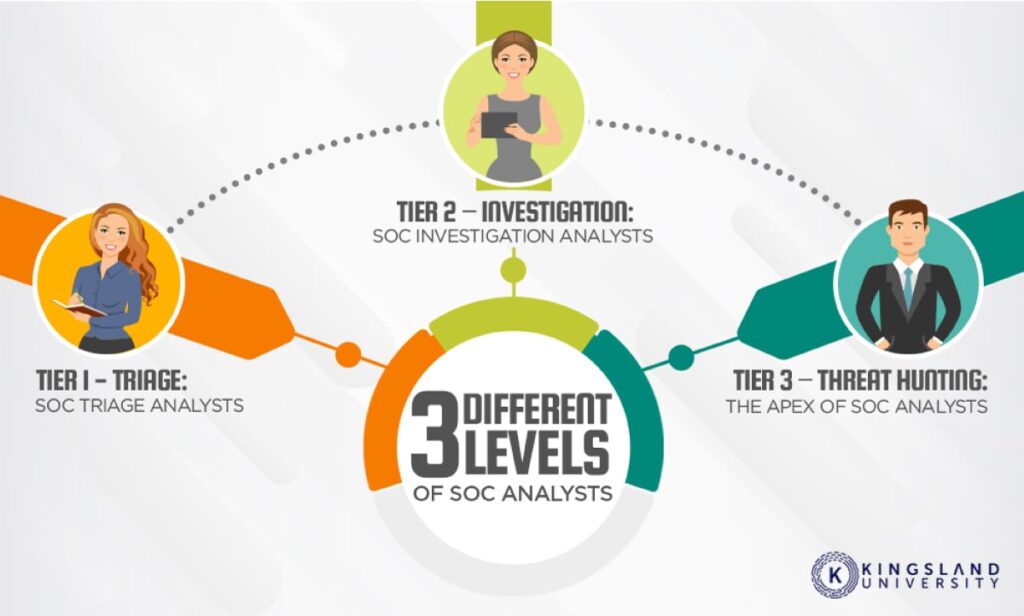
The security operations team may include several specialists depending on the size of the organization and what assets need to be monitored and protected. It can have chief rose like security operation center manager security engineers, security analysts and even threat hunters.
The overall goal of a security operations center is to collectively work together as a team monitoring and resolving issues, escalating issues where necessary to get them remediated asap, as they arise. From the entry level to the CEO everyone has a very important part to play collectively in the fight against cybersecurity threats.
How can automation benefit security operations monitoring?

Security automation is the machine-based execution of security actions which can detect, investigate, and remediate cyber threats with or without human intervention. When I think of this I think of a script placed in a crontab on a Linux system set to run to do automatic backup, logging, scan etc.
Security automation has the potential to identify incoming threat types and prioritize alerts as they emerge and perform automated incidents report response. This is essential as security automation can detect threats in the IT environment, it can group potential threat identifier by following the same workflow used by security analyst to investigate and classify events, and they can decide on the most important action to contain or mitigated threat and executing mitigation actions.
Security automation provides faster protection, faster containment and mitigation, improved productivity and security, and standardization of security processes. This can include automatic endpoint scans, automatic testing code generation, security automation rule updates for new environments.

Looking very closely at SOC, there are several automation techniques and tools that can be used in and around security operations monitoring. Monitoring syslog and /var/log/ directory to see log events that took place, monitoring firewalls events log files, monitoring, and analysis with Splunk, debugging tools, etc. automation comes into play on a Linux system, especially Kali, as you can create scripts to run and collect data on these tools, within the Linux platform.
An ‘complete’ application example of this would be robotic process automation RPA, which can automate lower level processes that do not require intelligent analysis, security orchestration automation and response ,SOAR, these systems provides solutions that enable organizations to collect data about security threats and respond to security incidents without human assistance, XDR extended detection response solutions are the evolution of endpoint detection and response EDR, and network detection and response NDR they consolidate data from across the security environment including endpoints networks and clouds allowing it to identify evasive attacks that hide between security layers.
